Telemedicine: definition, how it works, benefits, and challenges

Telemedicine represents one of the most significant transformations in the modern healthcare system, offering the ability to monitor, consult, and assist patients remotely through the use of digital technologies. It operates through secure platforms that enable the real-time collection and transmission of health data, facilitating communication between patients and healthcare professionals even outside hospital settings.
Key benefits include continuity of care, a reduction in avoidable hospitalizations, improved access to services in remote areas, and greater operational efficiency within the healthcare system. However, challenges remain, such as the need for adequate digital infrastructure, technological literacy among the population, and issues related to the protection of sensitive data.
Telemedicine is increasingly establishing itself as a structural component of clinical care, but its effectiveness depends on the ability to adapt organizational and regulatory models, as well as on acceptance by both users and healthcare professionals.
Artificial intelligence and wellness: a new paradigm for personal well-being
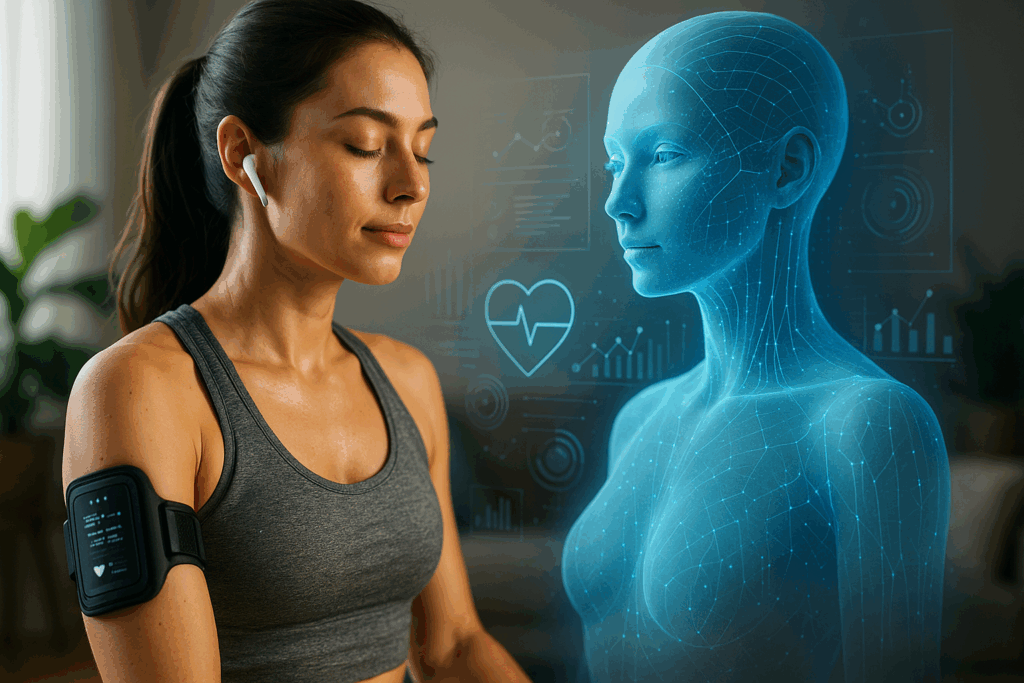

Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly central role in the wellness space, supporting the monitoring of physiological parameters, the personalization of wellness programs, and the optimization of individual performance. Its applications range from continuous biometric data collection to predictive analysis, with clear benefits for prevention and daily health management. Recent technological developments show how AI can be integrated into sports and fitness contexts to enhance awareness and performance. What is emerging is a transformation of the concept of well-being: increasingly data-driven, accessible, and tailored to individual needs.
Artificial intelligence and medicine: a strategic alliance for the future of health
Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in healthcare, helping improve diagnoses, treatments, and patient management. With the ability to process large volumes of clinical data, AI algorithms support healthcare professionals in areas such as radiology, oncology, and predictive and personalized medicine. This text explores the main applications, the expected benefits in terms of efficiency and accuracy, and the challenges related to ethics, regulation, and integration into clinical settings.
How remote monitoring and digital healthcare are transforming medical care in Italy
Digital healthcare and remote monitoring are transforming medical care in Italy, making treatment pathways more proactive, personalized, and accessible. Thanks to PNRR investments and the growing adoption of technologies such as telemedicine, wearable devices, and health data management platforms, doctors and patients can now collaborate more effectively, reducing avoidable hospitalizations and improving quality of life, especially for chronic patients. Regional initiatives and the development of national platforms like AGENAS are driving the system toward a more distributed model of territorial healthcare. Challenges remain around interoperability, training, and financial sustainability, but the benefits for the National Health Service and citizens are already clear.
Wellness and physiological monitoring: how to integrate technology and data into health pathways
Modern wellness is evolving through the integration of technology and physiological monitoring. The use of wearable devices and apps now makes it possible to collect real-time data and personalize increasingly effective wellness pathways. Continuous monitoring of vital parameters improves individual awareness, optimizes performance and promotes a sustainable lifestyle. Corporate wellness is also experiencing strong growth, with data-driven programs to support employee health. Trainers and fitness professionals are being called upon to build tailored experiences where technology and human connection integrate to offer a new way of experiencing wellness.
